On Android we can build what are called
Hybrid Apps. i.e. apps that have both HTML pages as well as native activities
co-existing. There is a lot of debate on which is the way to develop for
mobiles – HTML5 or native? Each of these have their own pros and cons. I will
not go into those now. However, to be able to embed HTML pages into your app,
one of the ways is through the use of a WebVew component.
Here I will share with you a very simple
example of building a WebView
App. This is nothing too different from what you see in the google
resources pages. However, the intention here is to move from this basic level
to a little more advanced level of interacting from the HTML page with Native
Apps – integrating through JavaScript. That will be in the next tutorial, in
keeping with my principle of explaining one thing at a time.
Also, for this example you will also need
to have a webserver that serves you some HTML pages that can be invoked through
your WebView.
As an addendum to this article, you will find how to create a small web server
app in your local environment.
Now, what is a WebView?
Google documentation beautifully explains it as
“A View
that displays web pages. This class is the basis upon which you can roll your
own web browser or simply display some online content within your Activity. It
uses the WebKit rendering engine to display web pages and includes methods to
navigate forward and backward through a history, zoom in and out, perform text
searches and more.”
Let’s create a WebView
which should display your home Page, on loading. In the main class of the
project here is the code in the onCreate() method:
public void onCreate(Bundle
savedInstanceState) {
Log.i(TAG, "Entering
onCreate");
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.webview);
mWebView = (WebView)findViewById(R.id.webview);
mWebView.clearCache(true);
mWebView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
mWebView.loadUrl("http://10.0.2.2:8080/SampleWebServer/Welcome.html");
Log.i(TAG,"Exiting
onCreate");
}
It is simple and straight forward. I have
defined a WebView
in the layout folder as below (file name webview.xml)
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<WebView
android:id="@+id/webview"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:scrollbarStyle="outsideOverlay"
android:scrollbarFadeDuration="5"
android:fillViewport="true"/>
</LinearLayout>
I get a
handle to the WebView
in this line: mWebView =
(WebView)findViewById(R.id.webview);
And
then I load the local URL in this line mWebView.loadUrl("http://10.0.2.2:8080/SampleWebServer/Welcome.html");
As simple as this. What this does is that
it invokes the default android browser if we have links on the welcome page as
shown below: (we have gone out of the WebView
into a browser app)
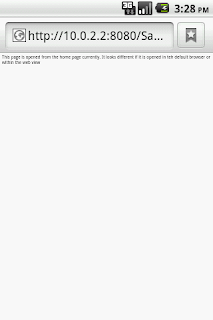
If we want to be able to continue opening
in the WebView,
here is the piece of code that would help. Basically we are writing out own
custom browser by extending the WebViewClient:
private class
WebViewSampleClient extends WebViewClient
{
@Override
public boolean shouldOverrideUrlLoading(WebView
view, String url) {
view.loadUrl(url);
return true;
}
}
Here we are telling to load the passed URL
into the WebView
by overriding the shoudlOverrideUrlLoading method of the WebViewClient.
After overriding the same, add another piece
of code into onCreate() method:
mWebView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewSampleClient());
after mWebView.loadUrl("http://10.0.2.2:8080/SampleWebServer/Welcome.html");
Now when you click on the Second Page link,
the new HTML page gets invoked within the WebView
as shown below:
From here, if you press a back button, you
will log out of the app, since WebView
is one activity and the pages are all opened within the WebView.
In order to override that behavior and you want to navigate back to the
HomePage within the WebView.
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode,
KeyEvent event) {
if ((keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK) && mWebView.canGoBack())
{
mWebView.goBack();
return true;
}
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode,
event);
}
Last but not the least, I have also added <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> into the AndroidManifest
file as this app will use the internet to invoke the http based URL.
NOTE: any webserver running locally can be
accessed through http protocol using the IP address 127.0.0.1 or localhost or
the actual IP address which you get when you run IP address command at the
command prompt. However, within the emulator, the linux kernel takes the
localhost as 10.0.2.2. and hence you will see in the code above that this IP
address is used.







